Introduction
Mention that this blog demonstrates how to build a chatbot that can respond with text, speech, and images while remembering conversation context.
Briefly introduce Agentic AI: LLMs that can plan, use tools, and have memory.
def chat(history):
messages = [{"role": "system", "content": system_message}] + history
response = openai.chat.completions.create(model=MODEL, messages=messages, tools=tools)
image = None
if response.choices[0].finish_reason=="tool_calls":
message = response.choices[0].message
response, city = handle_tool_call(message)
messages.append(message)
messages.append(response)
# artist will feedback The Image of the City
image = artist(city)
response = openai.chat.completions.create(model=MODEL, messages=messages)
reply = response.choices[0].message.content
history += [{"role":"assistant", "content":reply}]
# talker is Audio, let AI Speaks.
talker(reply)
return history, image1. Conversation and Memory
- Explain the concept of history: storing user messages and assistant replies.
- Show how Gradio passes this conversation history back and forth.
- Explain that maintaining the history simulates Memory, allowing context-aware responses in multi-turn conversations.
2. Tool: Speech Output with talker()
- Describe how the chatbot can speak its responses using TTS.
- Explain the steps:
- Call OpenAI TTS (
tts-1) with the message. - Decode MP3 audio in memory.
- Play audio using
simpleaudio(no temp files).
- Call OpenAI TTS (
- Emphasize how this makes the interaction more immersive.
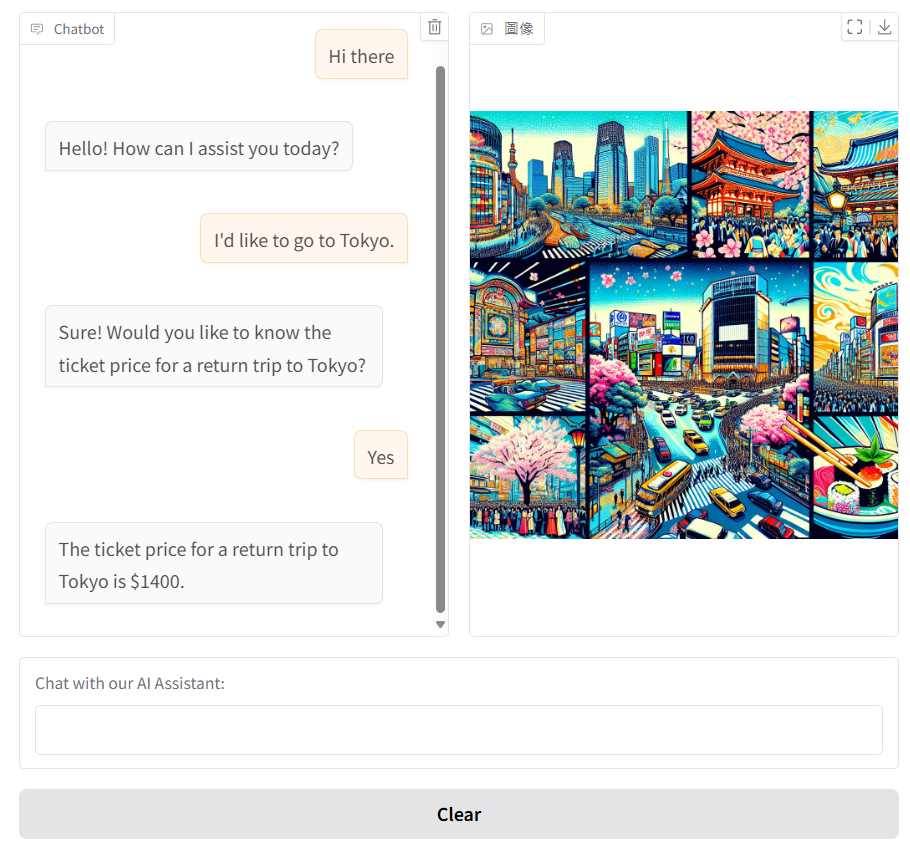
3. Tool: Image Generation with artist()
- Explain how the chatbot can generate images using DALL·E 3.
- Describe the process:
- Send a prompt (e.g., “a vacation in Paris”) to DALL·E 3.
- Decode base64 response into a
PIL.Image. - Display the image in Gradio.
- Highlight that the chatbot can now reply multimodally (text + visuals).
4. Chat Function Workflow
- Explain the logic of the
chat()function:- Combine system message + conversation history.
- Send messages to the LLM.
- Check for tool calls.
- Execute
talkerorartistif needed. - Append replies and tool outputs back to history.
- Return updated history and images.
- Mention how this design reflects planning and tool use in Agentic AI.
5. Bringing It All Together in Gradio
- Show how Gradio UI connects with the
chat()function. - Explain that:
- Users can continuously ask questions.
- The chatbot remembers previous turns (Memory).
- The chatbot can respond with text, play audio, and show images (Tools).
- Emphasize that this design demonstrates Agentic AI principles in practice.
Conclusion
- Recap how the chatbot combines Memory, Tool Use, and Multimodal Output.
- Mention that this is a foundation for more advanced agentic capabilities in future projects.
- Optional: hint at future expansions like planning, autonomous decision-making, or multi-agent collaboration.
Appendix
def artist(city):
image_response = openai.images.generate(
model="dall-e-3",
prompt=f"An image representing a vacation in {city}, showing tourist spots and everything unique about {city}, in a vibrant pop-art style",
size="1024x1024",
n=1,
response_format="b64_json",
)
image_base64 = image_response.data[0].b64_json
image_data = base64.b64decode(image_base64)
return Image.open(BytesIO(image_data))from io import BytesIO
import openai
from pydub import AudioSegment
import simpleaudio as sa
def talker(message: str):
# Call OpenAI TTS
response = openai.audio.speech.create(
model="tts-1",
voice="onyx", # or alloy
input=message
)
# Load MP3 into memory
audio_stream = BytesIO(response.content)
audio = AudioSegment.from_file(audio_stream, format="mp3")
# Play using simpleaudio (no temp file involved)
play_obj = sa.play_buffer(
audio.raw_data,
num_channels=audio.channels,
bytes_per_sample=audio.sample_width,
sample_rate=audio.frame_rate
)
play_obj.wait_done()import gradio as gr
# More involved Gradio code as we're not using the preset Chat interface!
# Passing in inbrowser=True in the last line will cause a Gradio window to pop up immediately.
with gr.Blocks() as ui:
with gr.Row():
chatbot = gr.Chatbot(height=500, type="messages")
image_output = gr.Image(height=500)
with gr.Row():
entry = gr.Textbox(label="Chat with our AI Assistant:")
with gr.Row():
clear = gr.Button("Clear")
def do_entry(message, history):
history += [{"role":"user", "content":message}]
return "", history
entry.submit(do_entry, inputs=[entry, chatbot], outputs=[entry, chatbot]).then(
chat, inputs=chatbot, outputs=[chatbot, image_output]
)
clear.click(lambda: None, inputs=None, outputs=chatbot, queue=False)
ui.launch(inbrowser=True)🔗 External Resources to Include
- Gradio Documentation: Chatbot Component
- Link: Gradio Chatbot Docs
- Description: Official documentation on Gradio’s chatbot component, detailing how to create interactive chat interfaces that support text, images, audio, and more.
- OpenAI’s Text-to-Speech Model (TTS-1)
- Link: OpenAI TTS-1
- Description: Information on OpenAI’s TTS-1 model, which powers text-to-speech functionalities, enabling natural-sounding voice responses.
- OpenAI’s DALL·E 3 Image Generation
- Link: OpenAI DALL·E 3
- Description: Details about DALL·E 3, OpenAI’s model for generating images from textual descriptions, useful for creating visual content in chatbots.
- Langchain: Memory Management for Chatbots
- Link: Langchain Memory Management
- Description: A tutorial on efficiently managing memory for chatbots using Langchain in Python, which can be beneficial for implementing memory features in your chatbot.
- Building Multimodal AI Agents
- Link: Building Multimodal AI Agents
- Description: An article discussing the development of AI agents that can process and respond with multiple modalities, including text, speech, and vision.
If you’d like to explore more tutorials like this, check out our AI category for related guides.