It be used for describing and matching patterns in the strings of text.
📌 Basic Syntax
javascript
const regex = /pattern/flags;pattern→ The regular expression pattern you want to match.flags→ Optional modifiers (e.g.,g,i,m, etc.)
const regex = /hello/i; // Case-insensitive match for "hello"
const text = "Hello World!";
console.log(regex.test(text)); // true🎯 Character Classes

javascript
const regex = /\d+/;
console.log("My age is 25".match(regex)); // ["25"]🔢 Quantifiers
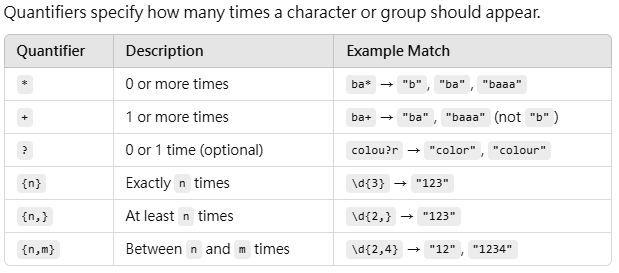
javascript
const regex = /\d{2,4}/;
console.log("My number is 1234".match(regex)); // ["1234"]🎯 Groups & Capturing

javascript
const regex = /(\d{3})-(\d{3})-(\d{4})/;
const match = "My phone is 123-456-7890".match(regex);
console.log(match[1]); // "123"
console.log(match[2]); // "456"
console.log(match[3]); // "7890"
const regex = /(?:abc)+/; //Avoid unnecessary memory usage when capture groups are not needed.
const text = "abcabcabc";
const match = text.match(regex);
console.log(match[0]); // "abcabcabc" (full match)
console.log(match[1]); // undefined (no capturing)
const regex = /(\b\w+)\s+\1/; // Capture a word, then match the same word again
const text = "hello hello world";
const match = text.match(regex);
console.log(match[0]); // "hello hello" (Full match)
console.log(match[1]); // "hello" (Captured word)
const regex = /^(\d)\1(\d)\2$/; // (\d)\1 → First digit must repeat (\d)\2 → Second digit must repeat.
console.log(regex.test("1122")); // true (1 repeats, 2 repeats)
console.log(regex.test("1132")); // false (1 repeats, but 3 ≠ 2)🚀 Assertions & Anchors
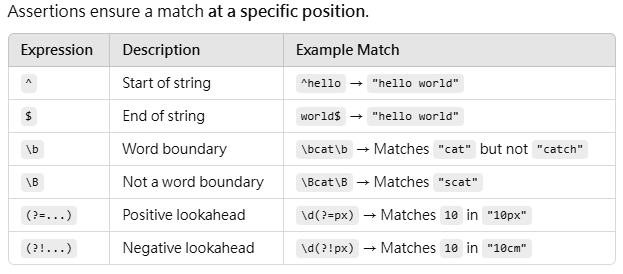
javascript
const regex = /\bcat\b/;
console.log("I love cats".match(regex)); // null (no exact match)
console.log("A cat is here".match(regex)); // ["cat"]🎏 Flags (Modifiers)

1. g – Global Flag
The global flag makes the regular expression search for all occurrences of the pattern in the string, rather than stopping after the first match.
javascript
const text = "abc abc abc";
const regex = /abc/g; // Global flag
const result = text.match(regex);
console.log(result); // ["abc", "abc", "abc"]2. i – Case-insensitive Flag
The case-insensitive flag allows the regular expression to match letters in any case (uppercase or lowercase).
javascript
const text = "AbC abc ABC";
const regex = /abc/i; // Case-insensitive flag
const result = text.match(regex);
console.log(result); // ["AbC"]3. m – Multiline Flag
The multiline flag changes the behavior of the anchors ^ (start of a string) and $ (end of a string) to work across multiple lines, not just the start and end of the entire string.
javascript
const text = "abc\nxyz";
const regex = /^abc/m; // Multiline flag
const result = text.match(regex);
console.log(result); // ["abc"]4. s – Dotall Flag
The dotall flag allows the dot (.) to match newline characters as well, meaning it will match any character, including line breaks (\n).
javascript
const text = "abc\ndef";
const regex = /abc.def/s; // Dotall flag
const result = text.match(regex);
console.log(result); // ["abc\ndef"]5. y – Sticky Flag
The sticky flag forces the regular expression to match only at the current position in the string. Unlike the global flag, which searches for all matches, the sticky flag makes sure the match begins at the current position.
javascritp
const text = "abcabcabc";
const regex = /abc/y; // Sticky flag
const result1 = regex.exec(text);
const result2 = regex.exec(text); // The regex will start searching where the previous match ended
console.log(result1); // ["abc"]
console.log(result2); // ["abc"]6. u – Unicode Flag
The unicode flag makes the regular expression treat the pattern as a Unicode pattern, allowing it to properly match Unicode characters beyond the basic ASCII set.
const text = "😀";
const regex = /\u{1F600}/u; // Unicode flag
const result = text.match(regex);
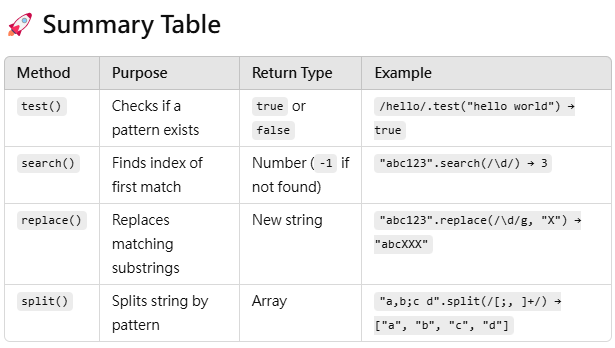
console.log(result); // ["😀"]1️⃣ test(): Check if a Pattern Exists
The test() method returns true if the pattern exists in the string, otherwise, it returns false.
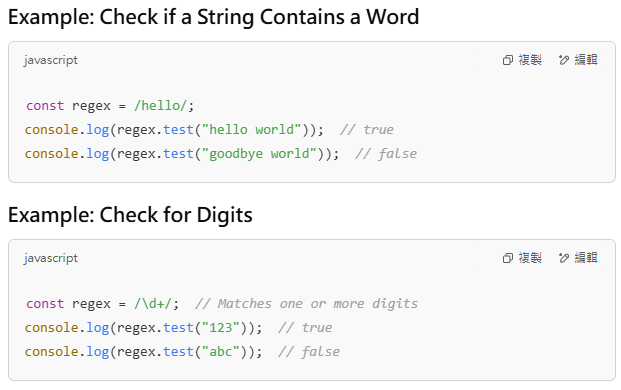
2️⃣ search(): Find Position of First Match
The search() method returns the index of the first match or -1 if no match is found.
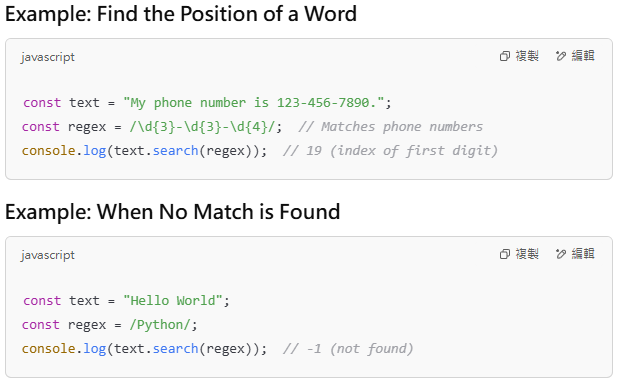
3️⃣ replace(): Replace Matching Substrings
The replace() method replaces matched text with a new string.

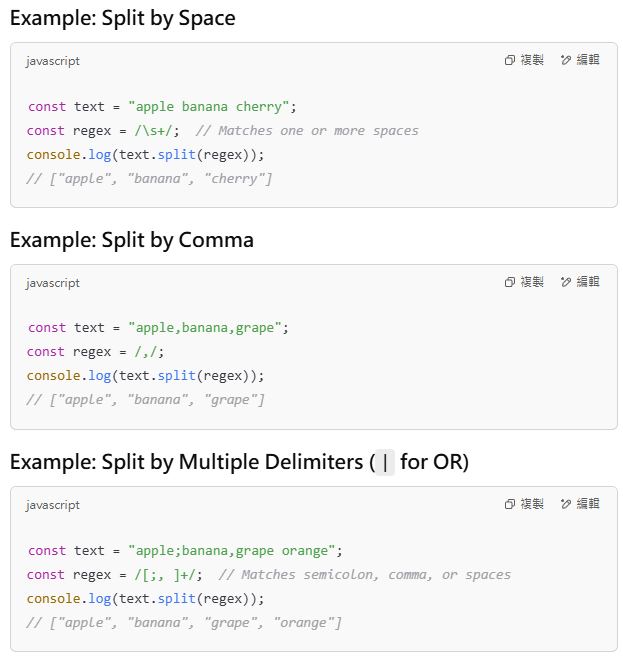
4️⃣ split(): Split a String into an Array
The split() method splits a string based on a regex pattern.